Computer programming languages are often confusing for beginners, each with its own dialect and vernacular.
And every programming language has its own set of syntax and code to write. So how to chose a programming language to learn?
With computer programming languages ranging from 67-year-old Assembly language to the young Ruby language.
And you know what? Every language has its own presence in the computer programming world.
Even a brief glance at the list of programming languages available gives one a nightmare. But for now, knowing the top programming languages to learn will help.
But then which is the best computer programming languages for beginners? or which programming language to learn first?
I decided to shortlist the most commonly used computer programming languages for beginners and make a complete guide to it.
Hope the list helps you.
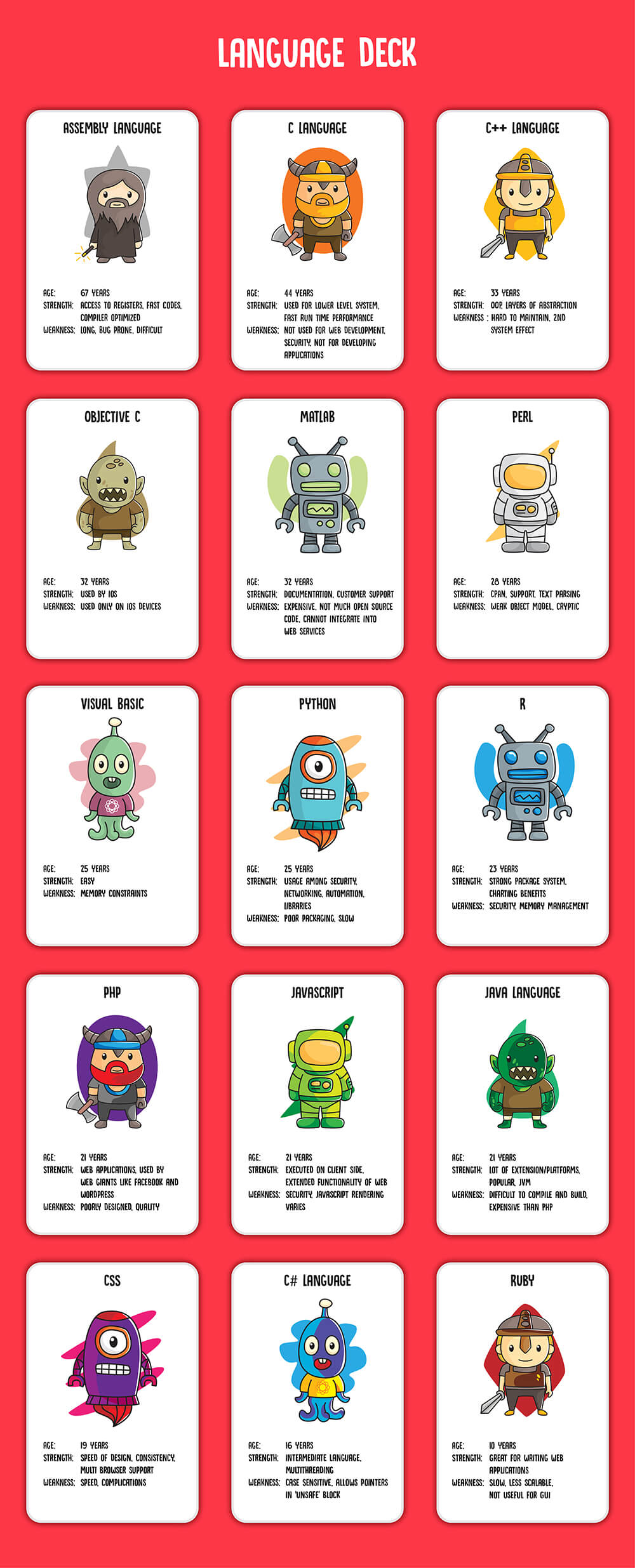
Check this computer programming deck for dummies before you read further about each of them in detail.
This will help you with a quick glance over each programming language.
-
Assembly Language
It was developed as a shorthand to machine language so that you don’t only have to remember 0’s and 1’s while coding.
Today, Assembly languages are used to access a specialized processor or address critical performance issues by direct hardware manipulation.
Typically, they are used in low-level embedded and real-time systems.
If you want to program a processor, the assembly language may not be necessary, but it is invaluable.
Major Organization Users: IBM, Apple
-
C++ Language
It is a middle-level, general purpose language. C++ brings in the feature of being object-oriented compared with its predecessor C.
C++ is popular in areas where graphical representation is required like that for Windows and Macintosh.
C++ has a rich function library and is a highly portable language.
Here is beginners guide to C++ - C++ language tutorial
Major Organization Users: Google, Mozilla, Firefox, Winamp, Adobe Software, Amazon, Lockheed Martin
-
C Language
It is a general-purpose programming language.
C provides a construct to map assembly language to C and has been most popularly used for operations which had been previously coded in assembly languages, including operating systems.
C is one of the most widely used languages and has been a great influence on its successors.
Major Organization Users: Microsoft, Apple, Oracle, Cisco, Raytheon
-
Objective C
It is a general-purpose, object-oriented programming language that adds Smalltalk-style messaging in C language.
Objective-C is one of the basic language used by Apple products and had been used in the development of iOS and OSX operating systems.
Major Organization Users: Apple
-
MATLAB
It integrates computation and programming in an easy-to-use environment where most of the objectives are represented by mathematical notation.
Matlab is a high-performance language and is typically used for mathematical computation and algorithm development.
Major Organization Users: GE, Continental, Robert Bosch, Honeywell, Mercedes-Benz
-
PERL
It is a scripting language with syntax similar to C and has many features of UNIX. Programs written in Perl are called Perl script.
Perl is an interpreted (not compiled) language that can optionally be compiled just before execution into either C code or cross-platform bytecode.
Major Organizations Users: Apple, Yahoo, BBC, IMDB
-
R
It is a dialect of S language. R language is used for statistical computing and graphics.
R is commonly used by statisticians and data miners for statistical and analysis.
R comes as a free software package and is available under GNU General public license.
Major Organizations Users: Google, GE, Dropbox
-
Visual Basic
It is a high-level language implemented on the .NET framework. VB was derived from BASIC, a user-friendly language designed for beginners.
It enables the rapid application development (RAD) of graphical user interface (GUI) applications and access to databases using objects.
Major Organizations Users: Microsoft
-
PYTHON
It is another interpreted language on this list. Developed as a general purpose language.
Python design emphasizes code readability and helps the user express in fewer lines of codes.
Major Organizations Users: Google, Pinterest, Instagram, YouTube, DropBox, NASA, ESRI
-
PHP
It is a scripting language used by users to create dynamic pages, which can be used further for transferring and submitting information on the web.
You can connect with servers, databases, and external websites based on IP address or information available.
PHP is one of the most commonly used scripting languages by web developers.
Major Organizations Users: Facebook, Google, GE, Wordpress
-
Javascript
It is a high-level programming language. Along with HTML and CSS, Javascript is one of the core languages in the development of World Wide Web content production.
Most of the websites support javascript without needing plugins.
Javascript is also used in the non-web-based application like PDF and desktop widgets.
Major Organizations Users: WordPress, Soundcloud, Linkedin, Groupon, Yahoo
-
C#
It is another language in the list of C languages. C# (pronounced as C-Sharp) is an object-oriented and component-oriented programming language.
C# is one of the programming languages developed for common language infrastructure.
Developers working on Windows prefer C# for developing applications and it turns out that C# is a big competitor to Java.
Major Organizations Users: Any company dealing extensively with Windows
-
CSS
CSS or Cascading style sheet is a style sheet language used for describing the presentation of documentation written in a markup language. Though often used for visual style up and user interface for HTML. CSS is a technology used by the most website to create visually engaging pages.
Major Organizations Users: Apple, CyberCoders, Apex Systems
-
Java
It is often called the best programming language, amidst much debate. Java is a high-level language. It was intended to be “write once, run anywhere (WORA),” i.e., once the code is written, it could be used on any platform that uses Java. Java is used for client-server applications with more than 9 million developers using the platform.
Major Organizations Users: V2COM, Eclipse Information Technologies, eBay, Eurotech
-
Ruby
It is one of the younger programming languages.
Developed to increase productivity, Ruby is a server interpreted, non-compiled programming language.
Ruby is used with Ruby on Rails for framework development.
Major Organizations Users: Cybercoders, Amazon, EMC, Bloomberg
-
SQL
Though not considered a programming language listed under Alan Turing test of programming language, for now, SQL is one of the recruiter's favorite programming language.
SQL, or Structured Query Language, is a special-purpose, domain-specific programming language used in programming and managing the database (DBMS).
Often described as a declarative language, SQL also includes procedural elements.
Despite being a standard in ANSI since 1986, most SQL code is not portable to among different database systems.
Major Organizations Users: Facebook, Google, Adobe, Alcatel-Lucent
You can also read about these 13 rare and underrated programming skills to learn here













































 Our AI-enabled Smart Browser takes frequent snapshots via the webcam, throughout the assessment.
Consequently, it is impossible to copy-paste code or impersonate a candidate.The browser prevents the following
candidate actions and facilitates thorough monitoring of the assessment:
Our AI-enabled Smart Browser takes frequent snapshots via the webcam, throughout the assessment.
Consequently, it is impossible to copy-paste code or impersonate a candidate.The browser prevents the following
candidate actions and facilitates thorough monitoring of the assessment:











